Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) is transforming diabetes management by providing a comprehensive approach to achieving optimal glycemic control. Traditional methods, such as finger-stick capillary glucose testing, offer limited insights into blood sugar levels, which can hinder effective diabetes management. CGM technology offers a more detailed picture by continuously tracking glucose levels and providing data on average glycemia, hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, and glucose variability. This wealth of information allows healthcare providers to tailor interventions more precisely, leading to better management of diabetes and a reduction in the risk of complications. Integrating CGM into primary care practices represents a significant advancement, moving from reactive to proactive management and fostering improved patient outcomes through personalized, data-driven strategies.
THE CRITICAL ROLE OF BLOOD SUGAR MONITORING:
Monitoring blood sugar levels is essential for maintaining overall health, particularly for individuals managing diabetes. Diabetes disrupts the body’s ability to produce or use insulin effectively, which is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels. Without proper management, individuals face increased risks of serious health issues, including heart disease, strokes, kidney failure, and blindness. A disciplined approach involving diet, exercise, and insulin therapy is vital for mitigating these risks. Continuous Glucose Monitoring CGM technology extends the benefits of blood sugar monitoring beyond diabetes management, highlighting its importance for general well-being and preventive health care. By offering real-time insights into how lifestyle choices affect blood sugar levels, CGM technology supports better health management and can help achieve weight management goals, enhancing overall health outcomes.
Understanding CGM Technology: A Leap Forward in Diabetes Management
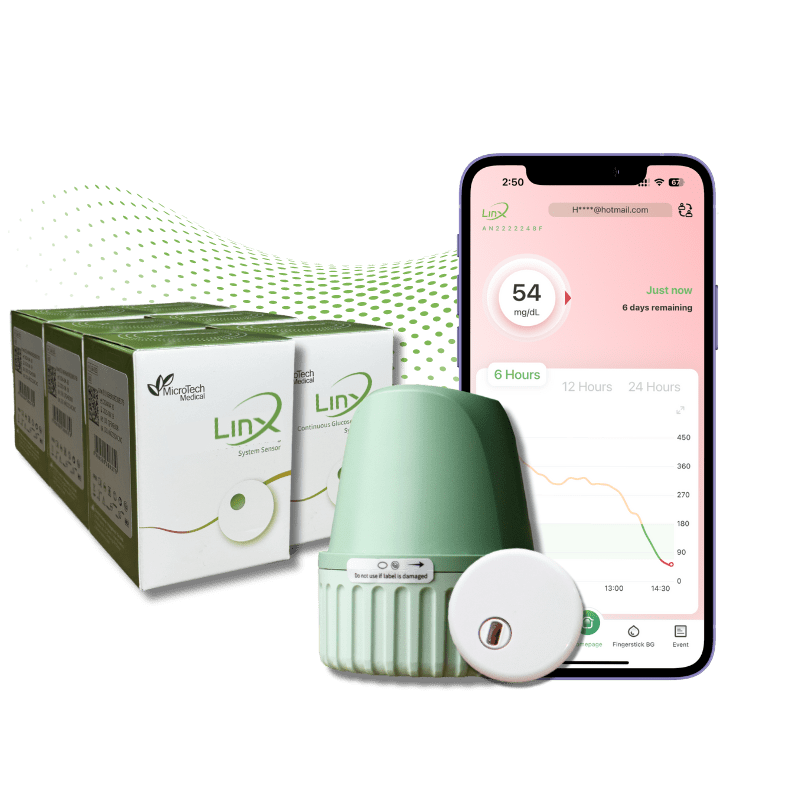
CGM technology is a game-changer in diabetes management, featuring compact wearable sensors that continuously monitor glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. These sensors, often considered among the best CGM devices available, are typically worn on the abdomen or arm and remain attached for a specified duration, providing uninterrupted glucose monitoring around the clock. The sensor contains a small electrode that interacts with glucose molecules, converting fluctuations into electronic signals. These signals are transmitted to a receiver or smartphone, where they are analyzed and displayed for the user. Advanced models, like the LinX CGM, enable users to receive real-time updates on their glucose levels, allowing for immediate adjustments to their diabetes management strategies. By offering continuous monitoring and prompt feedback, CGM technology helps users make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication, ultimately contributing to improved glycemic control and overall health.
OVERVIEW:
The integration of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) into primary care practices marks a pivotal shift in diabetes management, enhancing the ability to achieve optimal glycemic control and reduce complications. Unlike traditional finger-stick tests, CGM provides extensive data on average glycemia, hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, and glucose variability, enabling more precise and proactive treatment adjustments. Monitoring blood sugar is critical not only for managing diabetes but also for overall health, as stable blood sugar levels can prevent serious conditions such as heart disease and strokes. CGM extends these benefits beyond diabetes, emphasizing the universal value of consistent blood sugar regulation. CGM sensors, such as the LinX model, offer continuous, real-time glucose monitoring by using electrodes to detect and convert glucose fluctuations into data displayed on smartphones or receivers. This technology empowers users to make timely adjustments to their management routines, leading to better glycemic control and improved health outcomes.
FAQs
Q1: What is Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)?
A: CGM is a technology that continuously tracks glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, providing real-time data to help manage diabetes more effectively.
Q2: How does CGM differ from traditional blood sugar testing?
A: Unlike finger-stick tests that provide intermittent readings, CGM offers continuous monitoring and a more comprehensive view of glucose fluctuations throughout the day.
Q3: Can CGM technology benefit individuals without diabetes?
A: Yes, CGM can help anyone by providing insights into how lifestyle choices affect blood sugar levels, supporting better overall health and preventive care.
Q4: Where is the CGM sensor typically placed?
A: The sensor is usually worn on the abdomen or arm, where it continuously monitors glucose levels for a specified period.
 icons at the top right corner of the subsection.
icons at the top right corner of the subsection.